
Why Solar Energy?
Pakistan faces a persistent energy crisis characterized by frequent load shedding, escalating electricity costs, and overreliance on imported fossil fuels. Amid these challenges, solar energy emerges as a viable, sustainable, and cost-effective alternative. This article delves into the significance of solar energy for Pakistan, exploring its benefits, potential, and the transformative impact it can have on the nation’s energy landscape.
1. Understanding Solar Energy
Solar energy is harnessed by capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells are typically made from semiconductor materials like silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight, releasing electrons and generating an electric current. This clean and renewable energy source can power homes, businesses, and industries, reducing dependence on conventional energy sources.
2. The Energy Crisis in Pakistan
Pakistan’s energy sector grapples with several issues:
Frequent Power Outages: Many regions experience daily load shedding, disrupting daily life and economic activities.
Rising Electricity Costs: Electricity tariffs have surged, burdening consumers and businesses alike.
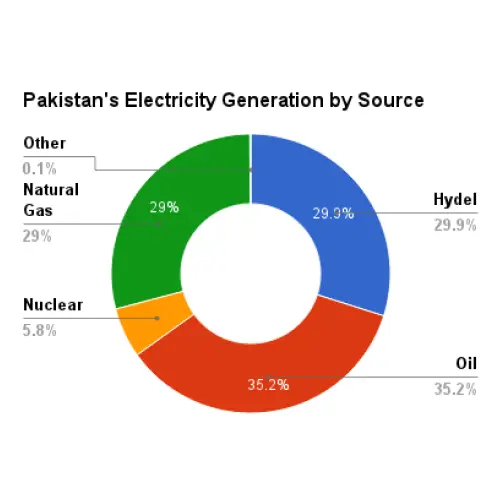
Dependence on Imported Fuels: A significant portion of electricity generation relies on imported fossil fuels, exposing the country to global price fluctuations and supply uncertainties.
These challenges underscore the urgent need for alternative energy solutions to ensure energy security and economic stability.
3. How Does a Solar Panel Work?
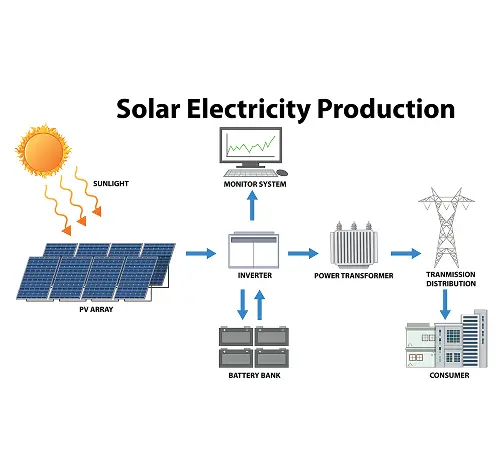
Solar panels work by capturing sunlight and converting it into usable electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. At the heart of each solar panel are photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are typically made from silicon — a natural element found in sand and one of the most abundant materials on Earth.
When sunlight strikes these PV cells, it energizes the electrons within the silicon layers. These layers are treated to create an electric field — one side has a positive charge, and the other has a negative charge. This difference in charge causes electrons to move, generating a flow of electricity. This is the fundamental principle behind how solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity.
energy source can power homes, businesses, and industries, reducing dependence on conventional energy sources.
4. Why Solar Energy is Ideal for Pakistan
Pakistan’s geographical location offers immense potential for solar energy:
Abundant Sunlight: The country receives an average solar irradiance of 5.3 kWh/m²/day, with many regions enjoying over 300 sunny days annually .
Diverse Applications: Solar energy can be utilized across various sectors, including residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural domains.
Decentralized Energy Production: Solar installations can be deployed in remote areas, providing electricity access to off-grid communities.
These factors make solar energy a practical and efficient solution for Pakistan’s energy needs.
5. Economic Benefits of Solar Energy
Investing in solar energy offers several economic advantages:
Reduced Electricity Bills: Solar panels can significantly lower monthly electricity expenses, with some households achieving near-zero bills.
Job Creation: The solar industry generates employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and sales.
Energy Independence: By harnessing local solar resources, Pakistan can reduce its reliance on imported fuels, enhancing energy security.
Moreover, the declining costs of solar panels and government incentives make solar energy increasingly accessible to a broader population.
